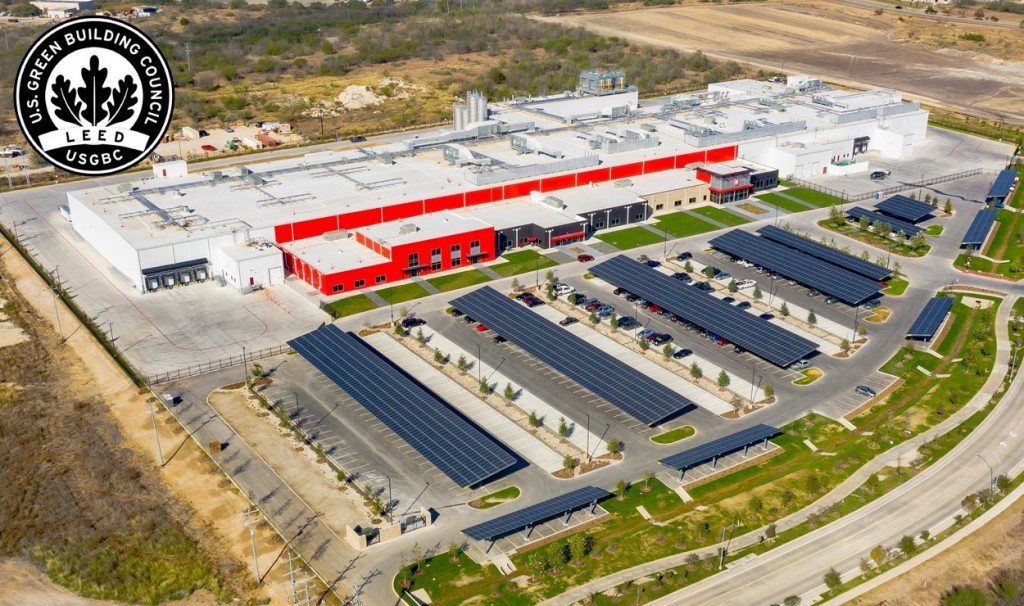
5 Energy Conservation Strategies for Food and Beverage Plants
A food processing operation requires more energy than some may realize. Unless you’re the plant owner paying the electricity bill, you might not have considered how much energy is needed to keep things running. Food production (agriculture, transportation, processing and handling) accounts for nearly 20% of all fossil fuel use in the United States, and 16% of that energy is used for food processing alone.
While utility costs are inevitable, there are strategies to make food and beverage plants more efficient and save money in the long run — though they often require an upfront investment. Energy savings are a long-term payback; it’s important to keep that in mind when building a plant or modifying a current one.
Continue Reading “5 Energy Conservation Strategies for Food and Beverage Plants”




![Inside the World’s Largest Sous Vide Processing Facility [PHOTOS]](https://stellarfoodforthought.net/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Cuisine-Solutions_01.jpg)